
It is the time during which the cell is preparing for division by undergoing both cell growth and DNA replication.Interphase is called the resting phase.It usually ends with division of cytoplasm.The M Phase or Mitosis starts with the nuclear division or karyokinesis.The interphase lasts more than 95% of the duration of cell cycle. In the 24 hour average duration of cell cycle of a human cell, cell division proper lasts for only about an hour.M Phase = Actual cell division or Mitosis. Interphase = Phase between two successive M phases. Yeast for example, can progress through the cell cycle in only about 90 minutes.īasic Phases of Cell Cycle – Interphase and M Phase or Mitosis.However, this duration of cell cycle can vary from organism to organism and also from cell type to cell type.A typical eukaryotic cell divides once in approximately every 24 hours.Įukaryotic vs Prokaryotic Cells: Eukaryotic vs.These events are themselves under genetic control.
#Prophase mitosis series#
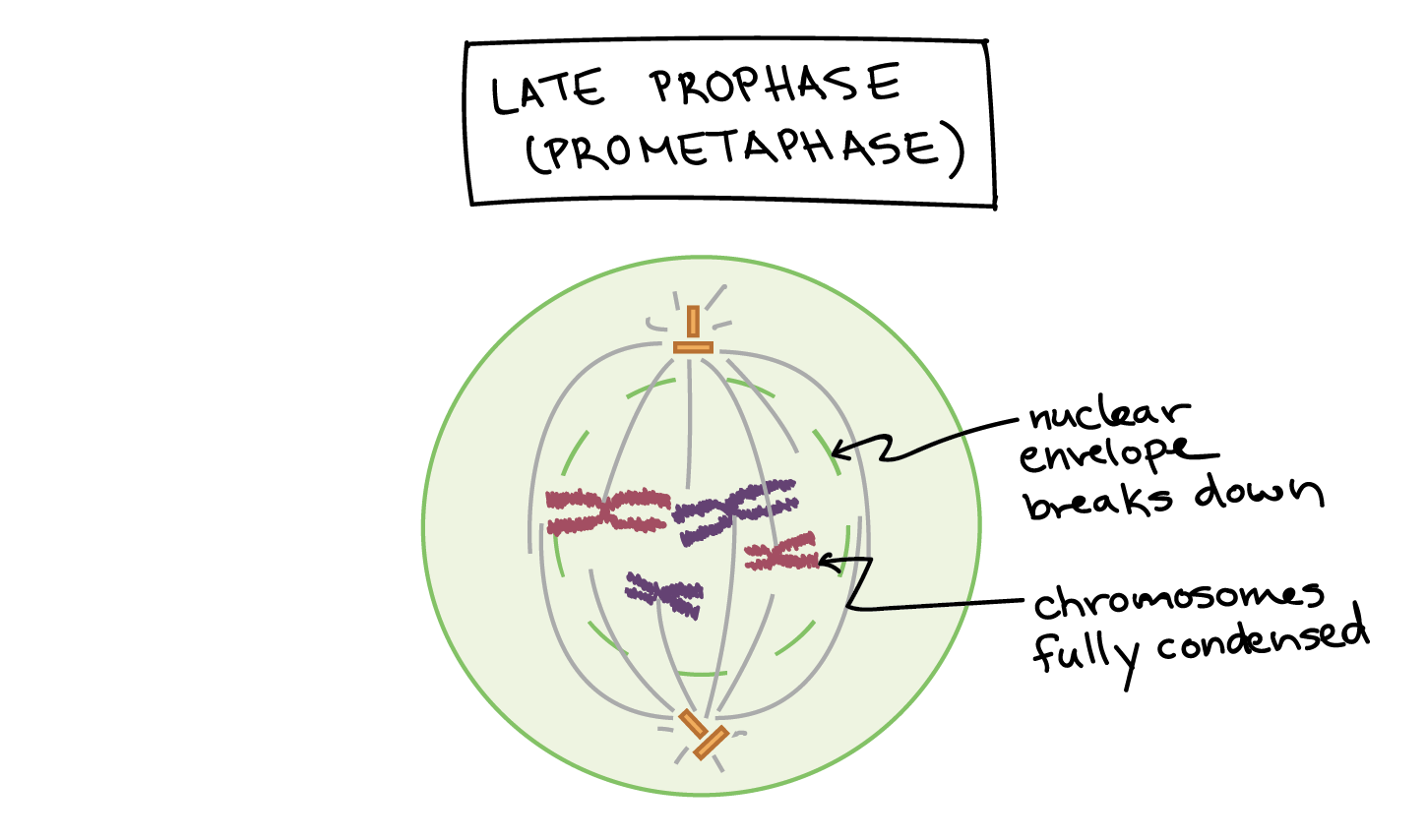
The replicated chromosomes (DNA) are then distributed to daughter nuclei by a complex series of events during cell division.Although cell growth (in terms of cytoplasmic increase) is a continuous process, DNA synthesis occurs only during one specific stage in the cell cycle.The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome, synthesizes the other constituents of the cell and eventually divides into two daughter cells is termed cell cycle.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
